Timber Gridshell
Friedberg, DE
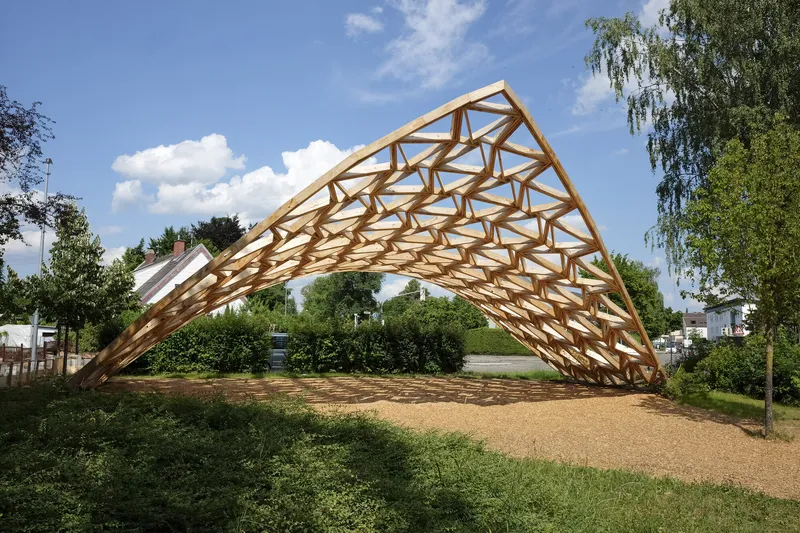
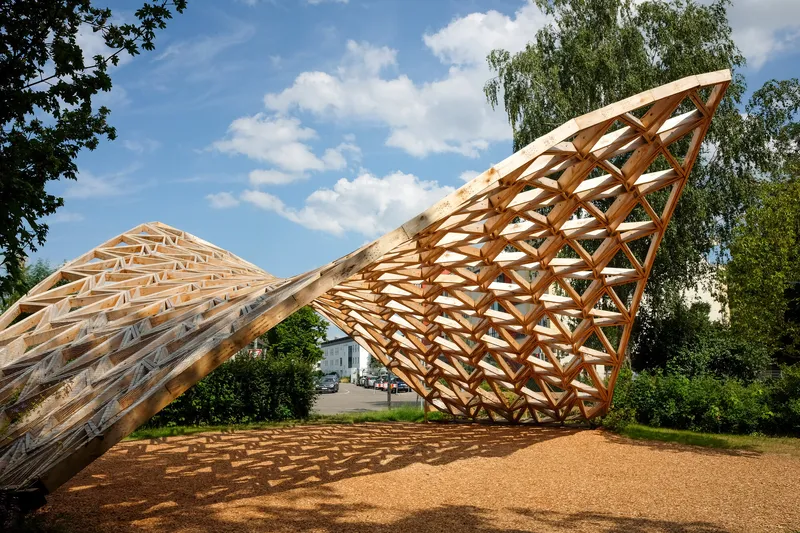
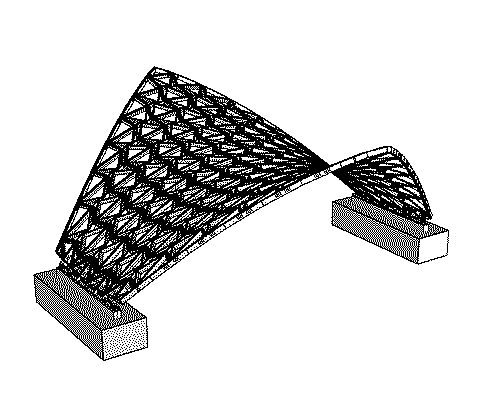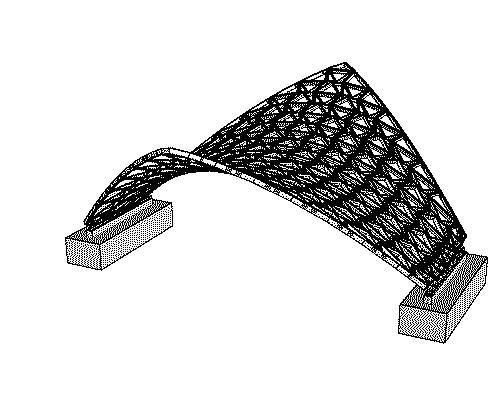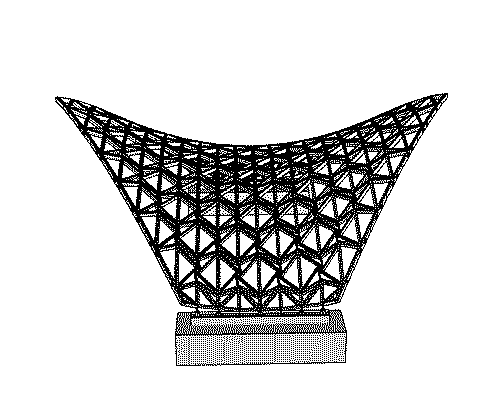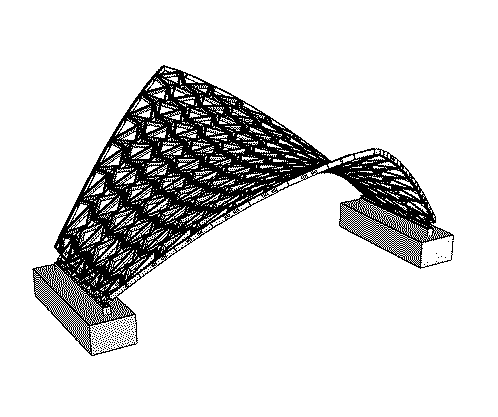
Geodesic hypar shell made of sweet chestnut wood – a combination of efficient load transfer, precise digital fabrication, and minimal material use
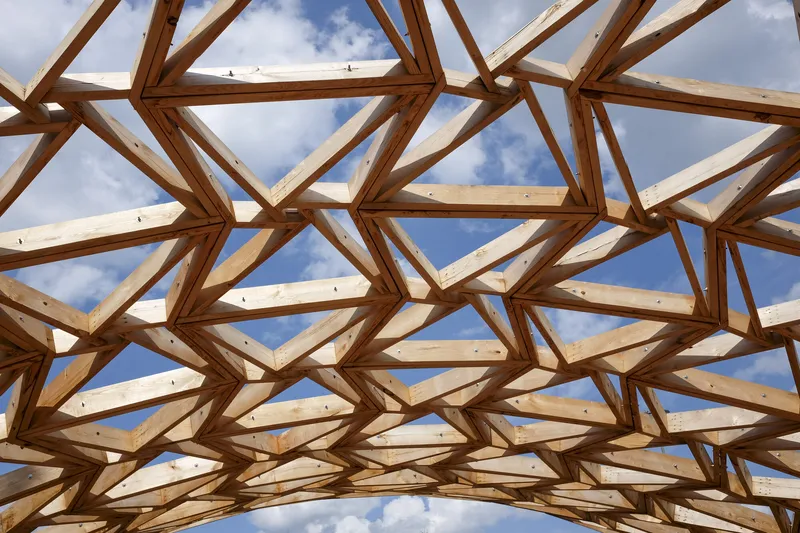
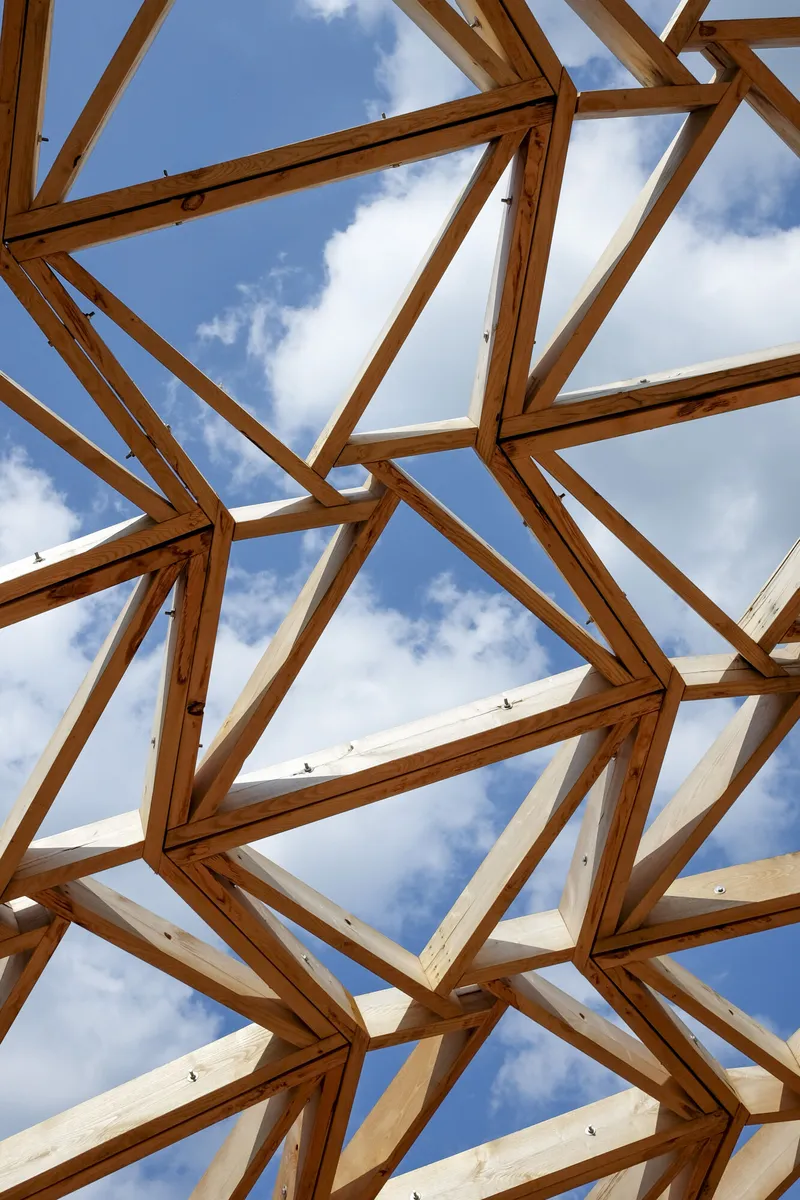
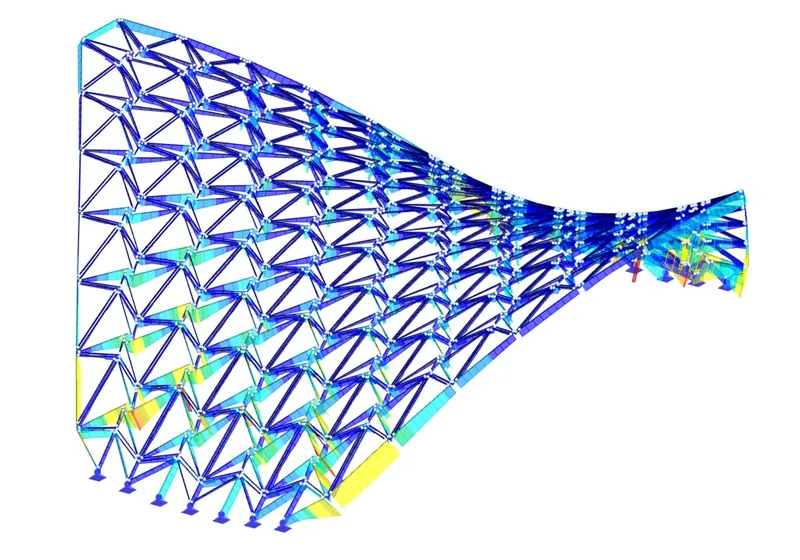
With a clear span of 15 meters and a height of 6 meters, the “Castanea Sativa Hypar” is currently the largest roof structure made from sweet chestnut wood. The geodesic form of the timber grid shell, consisting of a saddle surface, represents an efficient and resource-conserving way to span large distances with minimal material use. The roof shape of the shell is based on an anticlastic, hexagonal topology, stabilized by an interwoven cross-bracing system.
The choice of sweet chestnut (Castanea Sativa) as the main material for the structural framework is a response to the pressing challenges of modern construction, particularly the search for renewable, natural building materials from local wood, which offers higher resistance to drier climates and longer drought periods. Due to the natural growth form of hardwoods, which does not achieve the straightness of softwoods, the use of shorter individual elements is necessary. This requirement was addressed through the reciprocal roof geometry and could still be manufactured very efficiently through the use of modern digital fabrication techniques such as CNC machining and robotics.
For the static design of the grid shell, the permanent structure was dimensioned to withstand full wind and snow loads to ensure long-term operation under various climatic conditions. As part of the design process, different modeling approaches of the structure were compared, and based on that, a model of the entire load-bearing structure was developed, including the flexible coupling of the double struts and individual connection points between the hexagons, as well as compression contacts with tensile failure, to represent a realistic and detailed load transfer.
A central aspect of the construction of the weather-exposed load-bearing structure is the improved wood protection achieved through the use of spacers. All struts are spaced evenly 8 mm apart, allowing for necessary ventilation and protecting the wood surface from weather influences. This measure helps minimize the risk of moisture accumulation and resulting damage, ensuring the longevity of the wooden structure. The connections were made using stainless steel connectors and screws with special coatings due to the high tannin content of the wood.